抢先一步
VMware 提供培训和认证,助您加速进步。
了解更多Spring Security 以其高度可定制性而闻名,因此在我首次尝试使用 Google App Engine 时,我决定创建一个简单的应用程序,通过实现一些核心 Spring Security 接口来探索 GAE 的特性。在本文中,我们将了解如何
您应该已经熟悉将应用程序部署到 GAE。启动并运行一个基本应用程序不需要很长时间,您会在 GAE 网站上找到很多相关指南。
注册用户存储为 GAE 数据存储实体。首次认证时,新用户会被重定向到注册页面,在那里他们可以输入姓名。注册后,用户帐户可以在数据存储中被标记为“禁用”,即使他们已经通过 GAE 认证,也将无法使用该应用程序。
过滤器将认证决策委托给AuthenticationManager,它配置了一系列AuthenticationProviderbean,其中任何一个都可以认证用户,或者在认证失败时抛出异常。
对于基于表单的登录,AuthenticationEntryPoint只是将用户重定向到登录页面。认证过滤器(在此情况下是UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter)从提交的 POST 请求中提取用户名和密码。它们存储在一个Authentication对象中,并传递给一个AuthenticationProvider,它通常会将用户的密码与存储在数据库或 LDAP 服务器中的密码进行比较。
这就是组件之间的基本交互。这如何应用于 GAE 应用程序呢?
import com.google.appengine.api.users.UserService;
import com.google.appengine.api.users.UserServiceFactory;
public class GoogleAccountsAuthenticationEntryPoint implements AuthenticationEntryPoint {
public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException authException)
throws IOException, ServletException {
UserService userService = UserServiceFactory.getUserService();
response.sendRedirect(userService.createLoginURL(request.getRequestURI()));
}
}
如果我们将此添加到我们的配置中,利用 Spring Security 命名空间为此目的提供的特定钩子,我们将得到如下配置:
<b:beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security"
xmlns:b="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security http://www.springframework.org/schema/security/spring-security-3.1.xsd">
<http use-expressions="true" entry-point-ref="gaeEntryPoint">
<intercept-url pattern="/" access="permitAll" />
<intercept-url pattern="/**" access="hasRole('USER')" />
</http>
<b:bean id="gaeEntryPoint" class="samples.gae.security.GoogleAccountsAuthenticationEntryPoint" />
...
</b:beans>
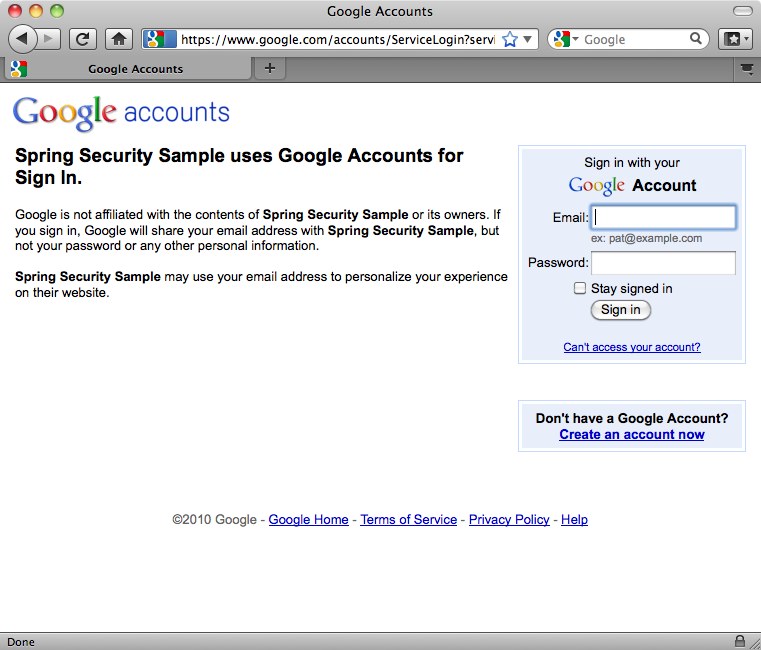
在这里,我们配置了除了 web 应用程序根目录之外的所有 URL 都需要“USER”角色。用户在首次尝试访问任何其他页面时将被重定向到 Google Accounts 登录屏幕
public class GaeAuthenticationFilter extends GenericFilterBean {
private static final String REGISTRATION_URL = "/register.htm";
private AuthenticationDetailsSource ads = new WebAuthenticationDetailsSource();
private AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;
private AuthenticationFailureHandler failureHandler = new SimpleUrlAuthenticationFailureHandler();
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
if (authentication == null) {
// User isn't authenticated. Check if there is a Google Accounts user
User googleUser = UserServiceFactory.getUserService().getCurrentUser();
if (googleUser != null) {
// User has returned after authenticating through GAE. Need to authenticate to Spring Security.
PreAuthenticatedAuthenticationToken token = new PreAuthenticatedAuthenticationToken(googleUser, null);
token.setDetails(ads.buildDetails(request));
try {
authentication = authenticationManager.authenticate(token);
// Setup the security context
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authentication);
// Send new users to the registration page.
if (authentication.getAuthorities().contains(AppRole.NEW_USER)) {
((HttpServletResponse) response).sendRedirect(REGISTRATION_URL);
return;
}
} catch (AuthenticationException e) {
// Authentication information was rejected by the authentication manager
failureHandler.onAuthenticationFailure((HttpServletRequest)request, (HttpServletResponse)response, e);
return;
}
}
}
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
public void setAuthenticationManager(AuthenticationManager authenticationManager) {
this.authenticationManager = authenticationManager;
}
public void setFailureHandler(AuthenticationFailureHandler failureHandler) {
this.failureHandler = failureHandler;
}
}
我们从头开始实现了这个过滤器,使其更容易理解,并避免了继承现有类的复杂性。如果用户当前未认证(从 Spring Security 的角度来看),过滤器会检查是否存在 GAE 用户(同样利用 GAE 的UserService)。如果找到,则将其封装到适当的认证令牌对象中(这里为了方便使用了 Spring Security 的PreAuthenticatedAuthenticationToken)并将其传递给AuthenticationManager由 Spring Security 进行认证。此时新用户将被重定向到注册页面。
该AuthenticationProvider实现与一个UserRegistry交互以存储和检索GaeUser对象(两者都特定于此示例)
public interface UserRegistry {
GaeUser findUser(String userId);
void registerUser(GaeUser newUser);
void removeUser(String userId);
}
public class GaeUser implements Serializable {
private final String userId;
private final String email;
private final String nickname;
private final String forename;
private final String surname;
private final Set<AppRole> authorities;
private final boolean enabled;
// Constructors and accessors omitted
...
该userId是 Google Accounts 分配的唯一 ID。电子邮件和昵称也从 GAE 用户那里获取。名字和姓氏在注册表单中输入。除非通过 GAE 数据存储管理控制台直接修改,“enabled”标志设置为“true”。AppRole是 Spring Security 的一个实现,即GrantedAuthority枚举
public enum AppRole implements GrantedAuthority {
ADMIN (0),
NEW_USER (1),
USER (2);
private int bit;
AppRole(int bit) {
this.bit = bit;
}
public String getAuthority() {
return toString();
}
}
角色的分配如上所述。该AuthenticationProvider看起来像这样
public class GoogleAccountsAuthenticationProvider implements AuthenticationProvider {
private UserRegistry userRegistry;
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
User googleUser = (User) authentication.getPrincipal();
GaeUser user = userRegistry.findUser(googleUser.getUserId());
if (user == null) {
// User not in registry. Needs to register
user = new GaeUser(googleUser.getUserId(), googleUser.getNickname(), googleUser.getEmail());
}
if (!user.isEnabled()) {
throw new DisabledException("Account is disabled");
}
return new GaeUserAuthentication(user, authentication.getDetails());
}
public final boolean supports(Class<?> authentication) {
return PreAuthenticatedAuthenticationToken.class.isAssignableFrom(authentication);
}
public void setUserRegistry(UserRegistry userRegistry) {
this.userRegistry = userRegistry;
}
}
该GaeUserAuthentication类是 Spring Security 的一个非常简单的实现,即Authentication接口,它将GaeUser对象作为 principal。如果您之前对 Spring Security 进行过一些定制,您可能会想知道为什么我们在此处没有实现UserDetailsService,以及为什么 principal 不是一个UserDetails实例。简单的回答是,您不必这样做——Spring Security 通常不介意对象的类型,而在这里我们选择直接实现AuthenticationProvider接口作为最简单的选项。
import com.google.appengine.api.datastore.*;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import samples.gae.security.AppRole;
import java.util.*;
public class GaeDatastoreUserRegistry implements UserRegistry {
private static final String USER_TYPE = "GaeUser";
private static final String USER_FORENAME = "forename";
private static final String USER_SURNAME = "surname";
private static final String USER_NICKNAME = "nickname";
private static final String USER_EMAIL = "email";
private static final String USER_ENABLED = "enabled";
private static final String USER_AUTHORITIES = "authorities";
public GaeUser findUser(String userId) {
Key key = KeyFactory.createKey(USER_TYPE, userId);
DatastoreService datastore = DatastoreServiceFactory.getDatastoreService();
try {
Entity user = datastore.get(key);
long binaryAuthorities = (Long)user.getProperty(USER_AUTHORITIES);
Set<AppRole> roles = EnumSet.noneOf(AppRole.class);
for (AppRole r : AppRole.values()) {
if ((binaryAuthorities & (1 << r.getBit())) != 0) {
roles.add(r);
}
}
GaeUser gaeUser = new GaeUser(
user.getKey().getName(),
(String)user.getProperty(USER_NICKNAME),
(String)user.getProperty(USER_EMAIL),
(String)user.getProperty(USER_FORENAME),
(String)user.getProperty(USER_SURNAME),
roles,
(Boolean)user.getProperty(USER_ENABLED));
return gaeUser;
} catch (EntityNotFoundException e) {
logger.debug(userId + " not found in datastore");
return null;
}
}
public void registerUser(GaeUser newUser) {
Key key = KeyFactory.createKey(USER_TYPE, newUser.getUserId());
Entity user = new Entity(key);
user.setProperty(USER_EMAIL, newUser.getEmail());
user.setProperty(USER_NICKNAME, newUser.getNickname());
user.setProperty(USER_FORENAME, newUser.getForename());
user.setProperty(USER_SURNAME, newUser.getSurname());
user.setUnindexedProperty(USER_ENABLED, newUser.isEnabled());
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> roles = newUser.getAuthorities();
long binaryAuthorities = 0;
for (GrantedAuthority r : roles) {
binaryAuthorities |= 1 << ((AppRole)r).getBit();
}
user.setUnindexedProperty(USER_AUTHORITIES, binaryAuthorities);
DatastoreService datastore = DatastoreServiceFactory.getDatastoreService();
datastore.put(user);
}
public void removeUser(String userId) {
DatastoreService datastore = DatastoreServiceFactory.getDatastoreService();
Key key = KeyFactory.createKey(USER_TYPE, userId);
datastore.delete(key);
}
}
正如我们之前提到的,示例使用枚举来表示应用程序角色。分配给用户的角色(权限)存储为一个EnumSet. EnumSet,它非常节省资源,用户的角色可以存储为一个简单的long值,从而简化了与数据存储 API 的交互。为此,我们为每个角色分配了一个单独的“bit”属性。
用户注册控制器包含以下方法,用于处理注册表单的提交。
@Autowired
private UserRegistry registry;
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String register(@Valid RegistrationForm form, BindingResult result) {
if (result.hasErrors()) {
return null;
}
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
GaeUser currentUser = (GaeUser)authentication.getPrincipal();
Set<AppRole> roles = EnumSet.of(AppRole.USER);
if (UserServiceFactory.getUserService().isUserAdmin()) {
roles.add(AppRole.ADMIN);
}
GaeUser user = new GaeUser(currentUser.getUserId(), currentUser.getNickname(), currentUser.getEmail(),
form.getForename(), form.getSurname(), roles, true);
registry.registerUser(user);
// Update the context with the full authentication
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(new GaeUserAuthentication(user, authentication.getDetails()));
return "redirect:/home.htm";
}
使用提供的名字和姓氏创建用户,并创建一组新的角色。如果 GAE 指示当前用户是应用程序的管理员,则其中也可能包含“ADMIN”角色。然后将其存储在用户注册表中,并且安全上下文会填充更新后的Authentication对象,以确保 Spring Security 了解新的角色信息并相应地应用其访问控制限制。
安全应用程序上下文现在看起来像这样
<http use-expressions="true" entry-point-ref="gaeEntryPoint">
<intercept-url pattern="/" access="permitAll" />
<intercept-url pattern="/register.htm*" access="hasRole('NEW_USER')" />
<intercept-url pattern="/**" access="hasRole('USER')" />
<custom-filter position="PRE_AUTH_FILTER" ref="gaeFilter" />
</http>
<b:bean id="gaeEntryPoint" class="samples.gae.security.GoogleAccountsAuthenticationEntryPoint" />
<b:bean id="gaeFilter" class="samples.gae.security.GaeAuthenticationFilter">
<b:property name="authenticationManager" ref="authenticationManager"/>
</b:bean>
<authentication-manager alias="authenticationManager">
<authentication-provider ref="gaeAuthenticationProvider"/>
</authentication-manager>
<b:bean id="gaeAuthenticationProvider" class="samples.gae.security.GoogleAccountsAuthenticationProvider">
<b:property name="userRegistry" ref="userRegistry" />
</b:bean>
<b:bean id="userRegistry" class="samples.gae.users.GaeDatastoreUserRegistry" />
您可以看到我们使用了custom-filter命名空间元素插入了我们的过滤器,声明了 provider 和 user registry,并将它们全部连接起来。我们还为注册控制器添加了一个 URL,该 URL 对新用户可见。
多年来,Spring Security 已经证明它具有足够的灵活性,可以在许多不同场景中增加价值,在 Google App Engine 中部署也不例外。同样值得记住的是,自己实现一些接口(就像我们在这里所做的那样)通常比尝试使用不太适合的现有类更好。您最终可能会得到一个更简洁的解决方案,它能更好地满足您的需求。
这里的重点是如何在启用 Spring Security 的应用程序中利用 Google App Engine API。我们没有涵盖应用程序工作原理的所有其他细节,但我鼓励您查看代码并亲身体验。如果您是 GAE 专家,随时欢迎提出改进建议!
示例代码已包含在 3.1 代码库中,您可以从我们的 git 仓库中查看。Spring Security 3.1 的第一个里程碑版本也应于本月晚些时候发布。